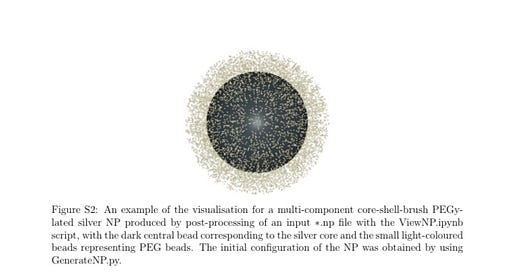
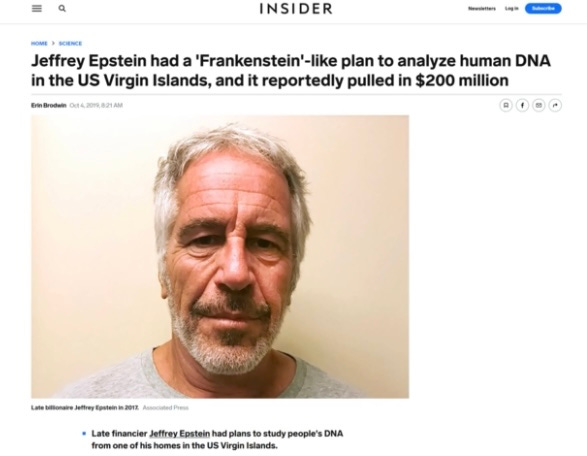
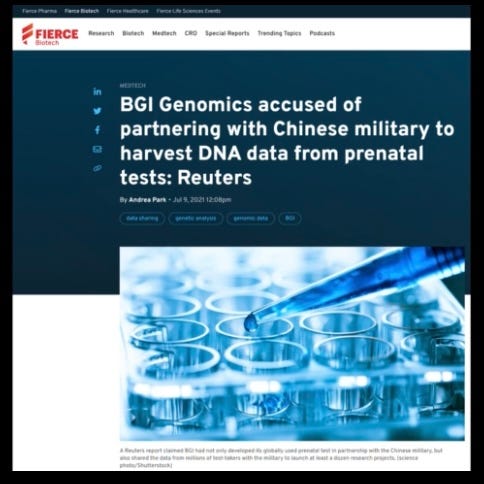
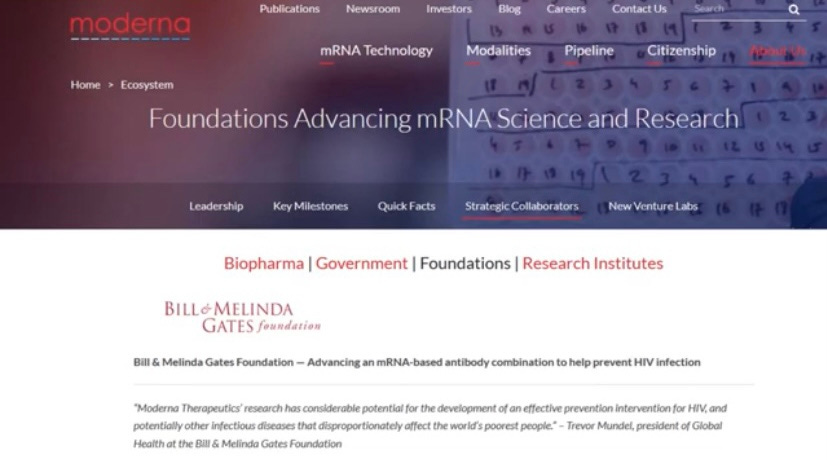
NPCoronaPredict: A Computational Pipeline for the Prediction of the Nanoparticle –Biomolecule CORONA
These Frankenstein Physicians playing god on our goods!
Nanotechnology, Ethics, and Environmental Health Symposium (Part 6) Please Watch this: https://mediapilot.georgetown.edu/ssdcms/i.do?u=a6029dfa7ba2491
We Know:
One Nanoparticle are so small that it can “infect” everything in his environment because they can enter every living cell without boundaries and therefore can manipulate the core and surface so that it is absolutely dangerous for all life on earth!
To Ask:
What does contamination & spreading really means?
Could it be that all nano technology is nothing more than atom physics on steroids?
Title: Understanding and Engineering the Nanoparticle Corona and Its Effect on Biological Interfaces
Presenter: Prof. Michael Strano, MIT
Abstract: Our lab at MIT has been interested in how nanoparticles in general and the 1D and 2D electronic structures of carbon nanotubes and graphene specifically, can be utilized to advance new concepts in molecular detection, including sensors, which we have recently applied to biomedical and agricultural problems. We introduce a method CoPhMoRe or Corona Phase Molecular Recognition1 as a method of discovering synthetic, heteropolymer corona phases that form molecular recognition sites at the nanoparticle interface, selected from a heteropolymer library. We show that certain synthetic heteropolymers, once constrained onto a single-walled carbon nanotube by chemical adsorption, also form a new corona phase that exhibits highly selective recognition for specific molecules. To prove the generality of this phenomenon, we report several examples of heteropolymers–nanotube recognition complexes for riboflavin, L-thyroxine, dopamine, nitric oxide, sugar alcohols, estradiol, as well as proteins such as fibrinogen. An emerging application of such sensor technology from my lab at MIT has been the use of near infrared fluorescent carbon nanotube sensors for in-vivo detection of a variety of biomolecules2. Here, we show that PEG-ligated d(AAAT)7 DNA wrapped SWNT are selective for nitric oxide, a vasodilator of blood vessels, and can be tail vein injected into mice and localized within the viable mouse liver. We demonstrate that a hydrogel encapsulated version of the sensor can remain viable and biocompatable in A129 mice for more than 400 days, opening the possibility of long term, persistent biochemical detection through thick tissue. Lastly, we discuss recent efforts in my laboratory to engineer plant systems using nanoparticles with specifically designed corona phases. We examine the subcellular uptake and kinetic trapping of a wide range of nanoparticles for the first time, using the plant chloroplast as a model system, but validated in vivo in living plants. We find that particle size and the magnitude, but not the sign, of the zeta potential are key in determining whether a particle is spontaneously and kinetically trapped within the organelle, despite the negative zeta potential of the envelope. We develop a mathematical model of this lipid exchange envelope and penetration (LEEP) mechanism, which agrees well with observations of this size and zeta potential dependence. The theory predicts a critical particle size below which the mechanism fails at all zeta potentials, explaining why nanoparticles are critical for this process. LEEP constitutes a powerful particulate transport and localization mechanism for nanoparticles within the plant system.
Bio: Professor Michael S. Strano is currently the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He received his B.S from Polytechnic University in Brooklyn, NY and Ph.D. from the University of Delaware bot in Chemical Engineering. He was a post doctoral research fellow at Rice University in the departments of Chemistry and Physics under the guidance of Nobel Laureate Richard E. Smalley. From 2003 to 2007, Michael was an Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign before moving to MIT. His research focuses on biomolecule/nanoparticle interactions and the surface chemistry of low dimensional systems, nano-electronics, nanoparticle separations, and applications of vibrational spectroscopy to nanotechnology. Michael recently completed a two year commitment with the Defense Science Study Group (DSSG) and is a current member of the Defense Science Board (DSB). He is the recipient of numerous awards for his work from 2005 to the present, including being recently named one of the world’s most influential scientific minds by Thomson Reuters.
________________
1. Zhang, JQ et. al. Molecular recognition using corona phase complexes made of synthetic polymers adsorbed on carbon nanotubes. Nature Nanotechnology, 8, 12, 2013, 959-968
2. Iverson, NM, et. al. In vivo biosensing via tissue-localizable near-infrared-fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nature Nanotechnology, 8, 11, 2013, 873
The Future is History
Policy Horizons | Horizons de politiques June 1, 2013
Faster, Cheaper Medicine through Synthetic Biology
Organs-on-demand with 3D Printing
Geoengineering the Climate
Really Smart Cars
Third-Generation Biofuels
The Rise of the Super-Soldier
Storing ‘Big Data’ in DNA
Solving Deep Problems with ‘Deep Learning’ Artificial Intelligence
https://horizons.service.canada.ca/en/2013/06/01/the-future-is-history/index.shtml
.
Published: 24 November 2013. Molecular recognition using corona phase complexes made of synthetic polymers adsorbed on carbon nanotubes.
https://www.google.com/search?q=corona+phase+molecular+recognition+2013&sca_esv=ab02dd2696e7e4b9&sxsrf=ACQVn08tLnr6tqznmGhopaezGlC8cIDZvQ%3A1711484300472&source=hp&ei=jC0DZtbKGvaP0PEP_bCOgAQ&oq=corona+phase+molecular+recognition+2013&gs_lp=EhFtb2JpbGUtZ3dzLXdpei1ocCInY29yb25hIHBoYXNlIG1vbGVjdWxhciByZWNvZ25pdGlvbiAyMDEzSP9gUL4KWNlecAF4AJABAZgB9AGgAcgfqgEGMC4zMS4xuAEDyAEA-AEBmAIfoALSIagCD8ICBxAjGOoCGCfCAgQQIxgnwgILEAAYgAQYsQMYgwHCAhEQLhiABBixAxiDARjHARjRA8ICCxAuGIAEGLEDGIMBwgILEC4YgwEYsQMYgATCAg4QABiABBiKBRixAxiDAcICEBAAGIAEGIoFGLEDGIMBGArCAggQLhiABBixA8ICBBAAGAPCAgsQLhiABBjHARivAcICBRAAGIAEwgILEC4YrwEYxwEYgATCAgcQABiABBgKwgIIEAAYgAQYxwPCAgYQABgWGB7CAggQABgWGB4YD8ICBRAhGKABwgILEAAYgAQYigUYhgPCAgQQIRgVmAMfkgcEMS4zMKAHldQB&sclient=mobile-gws-wiz-hp
Understanding and Engineering the Nanoparticle CORONA and Its Effect on Biological Interfaces MITnano – 2016 MITnano
The HSPH-NIEHS Nanosafety Center is a member of the Nanotechnology Health
The HSPH-NIEHS Nanosafety Center is a member of the Nanotechnology Health Implications Research (NHIR) consortium, which focuses on nanosafety research, and was established by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). The center brings together researchers from two of Harvard University’s schools (T.H. Chan School of Public Health [HSPH] and School of Engineering and Applied Sciences [SEAS]), Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), University of Maine (UM) and University of Florida (UF). The HSPH-NIEHS Nanosafety Center builds upon the nano-related infrastructure in these collaborating universities, developed over the past 10 years, which includes an interdisciplinary research group of faculty, research staff, and students, as well as state-of-the-art platforms for high-throughput synthesis of ENMs, including metal and metal oxides, cutting edge2D/3D ENMs such as CNTs and graphene, nanocellulose, and advanced nanocomposites, coupled with innovative tools to assess the fate and transport of ENMs in biological systems, statistical and exposure assessment tools, and novel in vitro and in vivo platforms for nanotoxicology research.
(2014) DOE CSGF: Understanding CORONA Phase Molecular Recognition Sensors on Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes – Krell Institute 2014
(2015) I.F.AKILDIZ ACM: CORONA: A Coordinate and Routing system for Nanonetworks
NANOCOM‘ 15: Proceedings of the Second Annual International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication September 2015
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2800795.2800809(2016) Understanding and Engineering the Nanoparticle CORONA and Its Effect on Biological Interfaces MITnano - MITnano
https://rumble.com/v4fviik-february-26-2024.html
(2017) CORONA PHASE MOLECULAR RECOGNITION nano BIOSENSORS 2017 MITnano - ENGINEERED BACTERIA FOR BIOSENSING IN THE IoBnT 2021 ITU (J-FET) U.N.
SENSE.nano Symposium 2017: Engineering the Nanoparticle Corona for Sensors
Professor Michael S. Strano is currently the Charles and Hilda Roddey Professor in the Chemical Engineering Department at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Funding
Grouping, Read-Across, Characterisation and clarification framework for regulatory risk assessment of manufactured nanomaterials and safer design of nano-enabled products (GRACIOUS), and Physiologically Anchored Tools for Realistic Nanomaterial Hazard Assessment (PATROLS),
Horizon 2020, European Commission, EUVisit Their Website
National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MDVisit Their Website
National Science Foundation, Arlington, VAVisit their website
Managing Risk of Nanomaterials,
Edinburg, United KingdomVisit their website
United States Department of Agriculture, Washington, DCVisit their website
National Institute of Food and Agriculture, Washington, DCVisit their website
U.S.A.F. BIOTECHNOLOGY: GENETICALLY ENGINEERED PATHOGENS (BIOWEAPONS)
(2010)
(Pg14) Future Application: 'Gene therapy is expected to gain in popularity. It will continue to
be improved upon and could unquestionably be chosen as a bioweapon. The rapid growth in
biotechnology could trigger more opportunities to find new ways to fight diseases or create new
ones'
(Pg14) Gene therapy as a Bioweapon:
'State of the Bioweapon: Stealth viruses just like the gene therapy, require a vector to be
inserted in the body and lay dormant until a trigger mechanism is activated either internally or
externally. Imagine having a cancer causing virus enter a human cell and lay dormant until an
external signal triggers the disease. When the signal gets activated the cells become abnormal
and could rapidly generate abnormal cell growth leading to a tumor and ultimately, death. Now,
apply this concept to a population where an HIV virus gets disseminated within a target
population. At a specific time chosen by the perpetrator, the signal would be triggered to harm
an entire population all at once. Although this bioweapon is futuristic it is not improbable and
deserves to be examined'
Medical inventor and author David Martin proves that the Pfiser and Moderna mRNA vaccines are not vaccines by medical definition and how Big Pharma is using national and state emergency authorizations to force these untested gene therapies onto the population.
https://odysee.com/@ARGONAUT:d/davidmartin:8
Gene Therapy
Because changes (mutations) of genes cause cancer, researchers are looking at ways to manipulate genes to fight cancer.
One form of gene therapy involves genetically modifying T cells (a type of immune cell)—see also Modified T cells. Doctors remove T cells from a person's blood and genetically modify them to recognize that person's specific cancer. When the modified T cells, called chimeric antigen receptor cells or CAR-T-cells, are put back in the person's bloodstream, they attack the cancer. CAR-T-cells can be used in people with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma.
New, still-experimental, techniques allow scientists to insert new genes into a cells, switch off abnormal genes, or increase the activity of helpful genes (see also Gene Therapy). Doctors hope these techniques may one day be useful for treating cancer.
Biotechnology: Genetically Engineered Pathogens (The Counterproliferation Papers, Future Warfare Series No. 53)
Corporate Author: USAF COUNTERPROLIFERATION CENTER MAXWELL AFB AL
Biotechnology: Genetically Engineered Pathogens (The Counterproliferation Papers, Future Warfare Series No. 53)
Number: ADA556597 | Open PDF
Abstract:
The bright side of advancements in biotechnology is offering great promise in improving human health, combating diseases, and promoting a better quality of life. But, for every bright side there is an opposing dark side. Biotechnology, when used maliciously or negligently, can destroy human life. Advanced biotechnology, in particular genetically engineered pathogens such as viruses, and bacteria, could become a potential choice for use as biological warfare agents. Will advancements in biotechnology enable genetically engineered pathogens to become a weapon of choice for nations, groups, andor individuals in 2035 In presenting the argument, a look into conventional biological warfare agents is necessary before focusing on advanced systems in determining the plausible role and effects of genetically engineered pathogens in the future. Characteristics of each pathogen will be discussed to determine the threats and challenges they may present by the year 2035. Rogue states, radical groups, and individuals, given the opportunity to employ biological weapons, will most likely use it to inflict harm and terror on the United States and its allies. Therefore, knowing what is to come will allow the United States to prepare for and deter the use of these nefarious weapons.
(2010) Since the early 2010s, DARPA has invested in a new type of vaccine technology — nucleic acid vaccines — which use the human body as its “bioreactor” to create the antibodies needed for immunity. DARPA funded this type of vaccine because traditional vaccine manufacturing is cumbersome, Jenkins said, and can take up to 18 months.
DARPA’s efforts on new mRNA vaccines have perhaps led to the best chance of effective immunization against COVID-19. This is in part thanks to a $25 million grant it awarded in 2013 to biotech company Moderna to manufacture mRNA vaccines to protect against a “wide range of known and unknown emerging infectious diseases and engineered biological threats."
https://www.c4isrnet.com/industry/2020/04/07/how-past-investments-positioned-darpa-to-take-on-coronavirus/
.
(2010) Electromagnetic wireless nanosensor networks
by IF Akyildiz · Cited by 802 — This paper provides an in-depth view on nanosensor technology and electromagnetic communication
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1109/MWC.2010.5675779
.
(2010) Nanobiotechnology: Tiny cell transistor
https://www.nature.com/articles/466904a
.
(2010) New nanoscale transistors allow sensitive probing inside cells
senior author Charles M. Lieber, the Mark Hyman, Jr. Professor of Chemistry at Harvard
Date:August 13, 2010Source:Harvard University https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/08/100812151626.htm
.
(2012) WHO: Nanotechnology and human health: Scientific evidence and risk governancehttps://nanopartikel.info/data/downloads/WHO-Report-Nanotechnology-and-Health-2012.pdf
.(2012) THz Intra Body Communication #IEEE 802.15.6 Frequency Bands
https://standards.ieee.org/ieee/802.15.6/5364/
.
(2012) IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks - Part 15.6: Wireless Body Area Networks
'Short-range, wireless communications in the vicinity of, or inside, a human body (but not limited to humans) are specified in this standard' https://standards.ieee.org/ieee/802.15.6/5364/
.
(2013) Ian F Akildiz IEEE - Tuning In to Graphene https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://ianakyildiz.com/bwn/papers/interviews/tuning-in-to-graphene.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwid06O617aEAxVsGtAFHfUOC8gQFnoECBUQAQ&usg=AOvVaw2cbIC10ni9PBMqFOXsQeFj
.
(2013) Ian F Akyildiz:
Graphene-based nano-antennas may enable networks of tiny machines
Peer-Reviewed Publication
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/858399(2016) A wireless body area network (WBAN) consists of low-power devices that are capable of sensing, processing, and wireless communication. WBANs can be used in many applications such as military, ubiquitous health care, entertainment, and sport. The IEEE Std 802.15.6-2012 is the latest international standard for WBAN
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/dac.3120
.
(2016) Klaus Schwab Anouces The Fourth Industrial Revolution)
' This Fourth Industrial Revolution is, however, fundamentally different. It is characterized by a range of new technologies that are fusing the physical, digital and biological worlds, impacting all disciplines, economies and industries, and even challenging ideas about what it means to be human'
https://www.weforum.org/about/the-fourth-industrial-revolution-by-klaus-schwab/
.
(2017) Industrial Cyberphysical Systems: A Backbone of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Cyberphysical systems (CPSs) are perceived as the pivotal enabler for a new era of real-time Internet-based communication and collaboration among value-chain participants, e.g., devices, systems, organizations, and humans
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7883993
.
(2017) ISO/IEC/IEEE 8802-15-6:2017
Information technology
Telecommunications and information exchange between systems
Local and metropolitan area networks
"This is a standard for short-range, wireless communication in the vicinity of, or inside, a human body (but not limited to humans)"
https://www.iso.org/standard/72352.html
.
(NASA 2017)
IEEE 802.15.6-based Prototype System for WBAN: Design and Implementation https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017arXiv170102421S/abstract
.
(2017) SENSE.nano Symposium: Engineering the Nanoparticle Corona for Sensors, Michael Strano - MIT.nano "CORONA PHASE MOLECULAR RECOGNITION"
https://rumble.com/v4am98u-january-31-2024.html
.
(2017) Evolving Nanoscale Communication
Biology, Engineering, and Robotics Converge #Bacteria
with Dr. Ian Akyildiz
JUN 05, 2017
https://legacy.iftf.org/future-now/article-detail/evolving-nanoscale-communication/
.
(2017)
Josep M. Jornet - An optofluidic channel model for in vivo nanosensor networks in human blood: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-Communication-of-nanomachines-inside-the-human-blood-b-Layered-RBC-Model_fig1_316652312
.
(2017) Ian F. Akyildiz
'The world will be totally different, with billions of nanoscaled devices circulating in the human body as additional red blood cells or white blood cells.'
#IntraBodyNanoNetworks
#IntrabodyMolecularCommunications
#MedicalBAN https://legacy.iftf.org/future-now/article-detail/evolving-nanoscale-communication/
.
(2018) #CORONA #WNSNs LaGOON: a simple energy-aware routing protocol for wireless nano-sensor networks
https://ietresearch.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1049/iet-wss.2018.5079
(VIDEO)https://rumble.com/v4dmr1t-february-15-2024.html
.
(2018) Nanonetworks in Biomedical Applications
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://par.nsf.gov/servlets/purl/10101417&ved=2ahUKEwj_stXYzLCEAxVMkYkEHWADAI44ChAWegQIChAB&usg=AOvVaw3jvSFHBbF3f3n5Gx5nUedZ
.
(2018) Josep M. Jornet - Nanonetworks in Biomedical Applications BIO-MOLECULAR COMMUNICATION NETWORKS #BioNanomachines https://par.nsf.gov/servlets/purl/10101417
.
(2018) Marzo, Jornet and Pierobon - Nanonetworks in Biomedical Applications. A molecular communication model for particulate Drug Delivery 'A particulate DDS takes advantage of the blood circulation in the cardiovascular system to propagate drug particles from the location where they have been injected into the blood flow, to the targeted site. Here, as shown in Figure 5, we describe a particulate DDS as three-fold process: injection, propagation, and delivery.'
https://par.nsf.gov/servlets/purl/10101417
.
(2018) 5G & Network Transformation Conference: Prof. Dr. Ian F. Akyıldız - Georgia Tech 2018 - 22min. Internet of Bio-NanoThings https://rumble.com/v465fuc-january-10-2024.html
.
(2019) Battelle-Led Team Wins DARPA Award to Develop Injectable, Bi-Directional Brain Computer Interface
COLUMBUS, Ohio (May 20, 2019)
https://www.battelle.org/insights/newsroom/press-release-details/battelle-led-team-wins-darpa-award-to-develop-injectable-bi-directional-brain-computer-interface
.
(2019) An Energy Balance Clustering Routing Protocol for Intra-Body Wireless Nanosensor Networks CORONA - NIH PMC
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6891516/
(VIDEO) https://rumble.com/v4d2cq0-february-12-2024.html
.
(2019) Electrochemical biosensor for CRISPR/Cas13a powered miRNA diagnostics | IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8956561
.
(2019) A biosynthetic dual-core cell computer | ETH Zurich
https://ethz.ch/en/news-and-events/eth-news/news/2019/04/biosynthetic-dual-core-cell-computer.html
.
(2019) U.S. patent application number 16/876114 was filed with the patent office for system and method for testing for covid-19. The applicant listed for this patent is Richard A. Rothschild. Invention is credited to Richard A. Rothschild. #WideAreaNetwork https://uspto.report/patent/app/20200279585#D00000
.
(2020) Ian F Akyildiz: ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies (ITU J-FET) U.N.
https://www.itu.int/en/journal/j-fet/Pages/default.aspx
Answer: Equilibration is a method of normalizing the sensor and system so that the output of every sensing element is the same when a uniform pressure is applied. The software then determines a unique scale factor for that sensing element to compensate for the slight variation.
October 29, 2019, a panel of „experts“ that included Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Margaret Hamburg, former FDA commissioner, Rick Bright, director of Department of Health and Human Services Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, Bruce Gellin, president of Sabin Vaccine Institute, Michael Specter, staff writer, New Yorker Magazine, and Casey Wright, CEO of Flu Lab, gathered at the Milken Institute to discuss how to get the public to accept quickly produced and untested MRNA-based vaccines. Calling it the flu was not enough, they concluded: they needed a „disruptive event.“
This is not a conspiracy theory documentary. It is a conspiracy fact official video released on C-Span.
Let the experts speak. Listen to them.
Donald Trump was paid by Pfizer to promote the covid-19 vaccine
https://docquery.fec.gov/pdf/286/201704180300150286/201704180300150286.pdf
This link will show you a PDF file of the entire list of donors who donated money to Donald Trump in the 58th presidential inaugural committee, prior to his inauguration. In page 163 of the document, Pfizer's NYC headquarters address as well as the money they donated are on the page, with the amount being listed as exactly 1,000,000$ USD. It also lists the date from when he received it, which states it as December 22, 2016.
.
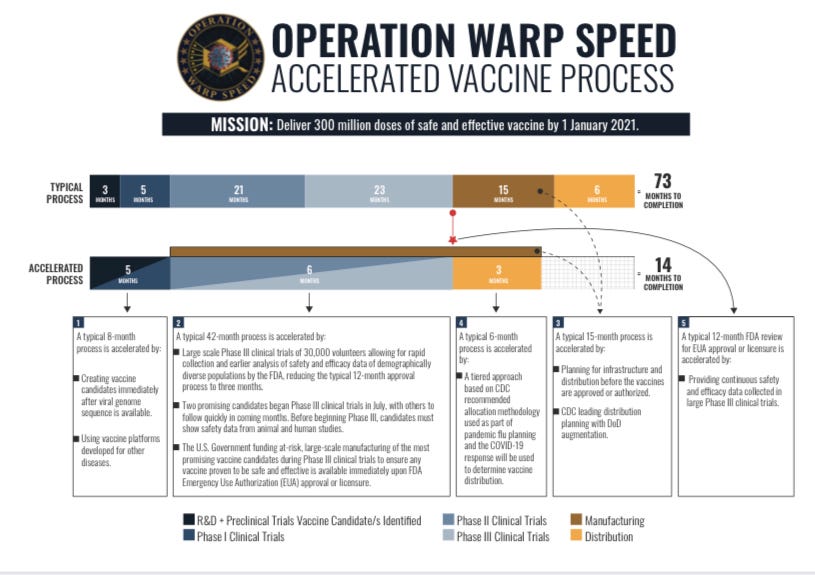
Ivanka Trump admits her father’s administration partnered with Moderna to produce mRNA vaccines BEFORE Operation Warp Speed
https://www.naturalnews.com/2023-01-18-trump-moderna-mrna-vaccines-operation-warp-speed.html
.
Donald J. Trump
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/authors/donald-j-trump
.
2018 ‘Warp speed’ technology must be ‘force for good’ UN chief tells web leaders | UN News https://news.un.org/en/story/2018/11/1024982
👀
.
(2017) President Trump Signs Bill Overturning Internet Privacy Protections
https://time.com/4724128/donald-trump-internet-history-isp-privacy-browser-history/
REMDESIVIR AND OTHER NANOTECHNOLOGIES
FEB 8
NANOTECHNOLOGY HAS BEEN USED IN EVERYTHING IN THIS „PANDEMIC“ https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/adfm.202107826
(https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202107826) Nanoscience versus Viruses: The SARS-CoV-2 Case First published: 13 December 2022
State-of-the-art in design rules for drug delivery platforms: Lessons learned from FDA-approved nanomedicines
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168365914003393?via%3Dihub
20 Years NNI
https://www.nano.gov/
NNI Retrospective Video: Creating a National Initiative (Trailer 3 min.)
Building Better Agriculture One Atom at a Time
Watch Home
NNI Supplement to the President’s 2024 Budget
March 05, 2024
Description
This document is a supplement to the President’s 2024 Budget request and serves as the Annual Report for the National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI), called for under the provisions of the 21st Century Nanotechnology Research and Development Act (15 USC §7501). The report also addresses the requirement for Department of Defense reporting on its nanotechnology investments, per 10 USC §2358.
The President’s 2024 Budget requests an all-time record of $2.16 billion for the NNI, with a sustained investment in foundational research that will fuel new discoveries, and increasing investments in application-driven R&D to advance technologies of the future and address national priorities. Cumulative NNI funding since its inception in 2001 totals over $43 billion (including the 2024 request). The President’s 2024 Budget supports nanoscale science, engineering, and technology R&D at 11 agencies. See the graph at right for funding trends since the inception of the NNI. The NNI Supplement to the President’s 2024 Budget documents progress of the NNI participating agencies in addressing the goals and objectives of the NNI. As called for in the 21st Century Nanotechnology Research and Development Act, the report also reviews current and planned investments of NNI participating agencies by Program Component Area (PCA).
About the cover images (above)
Each year’s NNI Supplement to the President’s Budget features cover images illustrating recent developments in nanotechnology stemming from NNI activities that have the potential to make major contributions to national priorities.
This year’s front cover (above, right side) includes a scanning electron microscope image of halide perovskite crystals grown directly onto surfaces with precise alignment, enabling the fabrication of nanoscale light-emitting diodes (nanoLEDs). The image was initially taken by the Farnaz Niroui Group at MIT, then rendered by a graphic artist to make the final cover art. Credit: Sampson Wilcox, Research Laboratory of Electronics at MIT. The back cover (above, left side) is an electroluminescent image of the nanoLED arrays in operation taken with an optical microscope, where the crystals are not visible at this resolution, but their light emission is visible. Credit: the Farnaz Niroui Group at MIT. Potential applications include light-emitting diodes, lasers, on-chip quantum light sources, photodetectors, and memristors. The work was supported by NSF and used facilities of NSF’s National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure (NNCI). For more information see: https://news.mit.edu/2023/researchers-grow-precise-arrays-nanoleds-0706 and https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39488-0.
About the inside back cover (above)
Images illustrate examples of NNI outreach activities. The NNI promotes public outreach to students, teachers, the general public, and the NNI community.
Top left – The NNI’s Nano4EARTH National Nanotechnology Challenge is gathering insights from the research community and the public on opportunities for harnessing nanotechnology to address the challenges of climate change (https://www.nano.gov/nano4EARTH).
Top right – The NanoEducators Quarterly Forums, organized through the NNI’s Teachers Network, provide teachers with opportunities for community building, ideas for classroom experiments, and engagement with nanotechnology researchers (https://www.nano.gov/teachersnetwork).
Upper middle right – National Nanotechnology Day is an annual event featuring community-led events and activities on or around October 9 to help raise awareness of nanotechnology, its use in products that enrich our daily lives, and the challenges and opportunities for the future (https://www.nano.gov/nationalnanotechnologyday).
Middle left – The „Stories from the NNI“ podcast consists of conversations with experts from K–12 and higher education institutions, government, non-profit organizations, or industry. Shown here are two recent podcasts (https://nano.gov/podcasts).
Lower middle right – The NNI is in the process of refreshing its strategy for nanotechnology-related environmental, health, and safety research, including seeking input from the public and the research community through a public workshop held in 2023 (https://www.nano.gov/2011EHSStrategy).
Lower left – The annual Student Leaders Conference in 2023 included a career pathways panel with academia, industry, and government leaders; a hands-on session on FAIR (Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reuse) data principles; and a poster session (https://nexttechnetwork.org/slc/).
Lower right – The September 2023 Nanotechnology Infrastructure Leaders Summit included directors and other leaders from user facilities and manufacturing institutes, representing nanotechnology user facilities funded by DOE, NSF, NIST, and NIH; light and neutron centers; and Manufacturing USA institutes (https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/news-updates/2023/10/06/readout-of-the-nanotechnology-infrastructure-leaders-summit/).
File Downloads
Harari: What Do We Do With The Useless Eaters?
And don’t forget Palantir and big tech are buy up and controlling all of our health data, Bill Gates and 23&me recorded our DNA and philanthropist with ISpy payed hospitals and carehomes to make experiments on human beings.
Updated June 8, 2023: Blackrock Neurotech has pioneered the use of brain-computer interface (BCI) technology similar to Neuralink. Blackrock Neurotech received FDA 510k clearance for use in humans in 2007. Per Blackrock Neurotech, the company is not affiliated with Blackrock. Blackrock Neurotech is funded by billionaire Peter Thiel who is Elon Musk’s former partner at PayPal.
June 7, 2023: Electrode implants into civilians’ brains didn’t just receive FDA clearance with Neuralink. The flagship brain-computer interface (BCI) technology behind Musk’s Neuralink technologies is called NeuroPort Array and is owned by Blackrock Neurotech.
Former President, Barack Obama is a leader in brain-computer interface (BCI) technologies and active with Blackrock Neurotech.
https://unlimitedhangout.com/2024/07/investigative-reports/the-man-behind-trumps-vp-pick-its-worse-than-you-think/
How nice that the same Corporation for health like the nazis for the Holocaust used ibm worked now on medicine such as mRNA and tablets out of the printer with the information from yes Palantir to use this data to mix your privatized no clinical trails treatments especially in an emergency and carbyn holds the 9-1-1 line…. Halleluja this future sucks!
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/nanobots
Evidence of Crimes Against Humanity – Darkfield Blood Microscopy